Our API Ecosystem is More Fragile Than We Think
By Naresh Jain
API resiliency testing: how to keep your services standing when dependencies fail
The fragile truth about modern systems
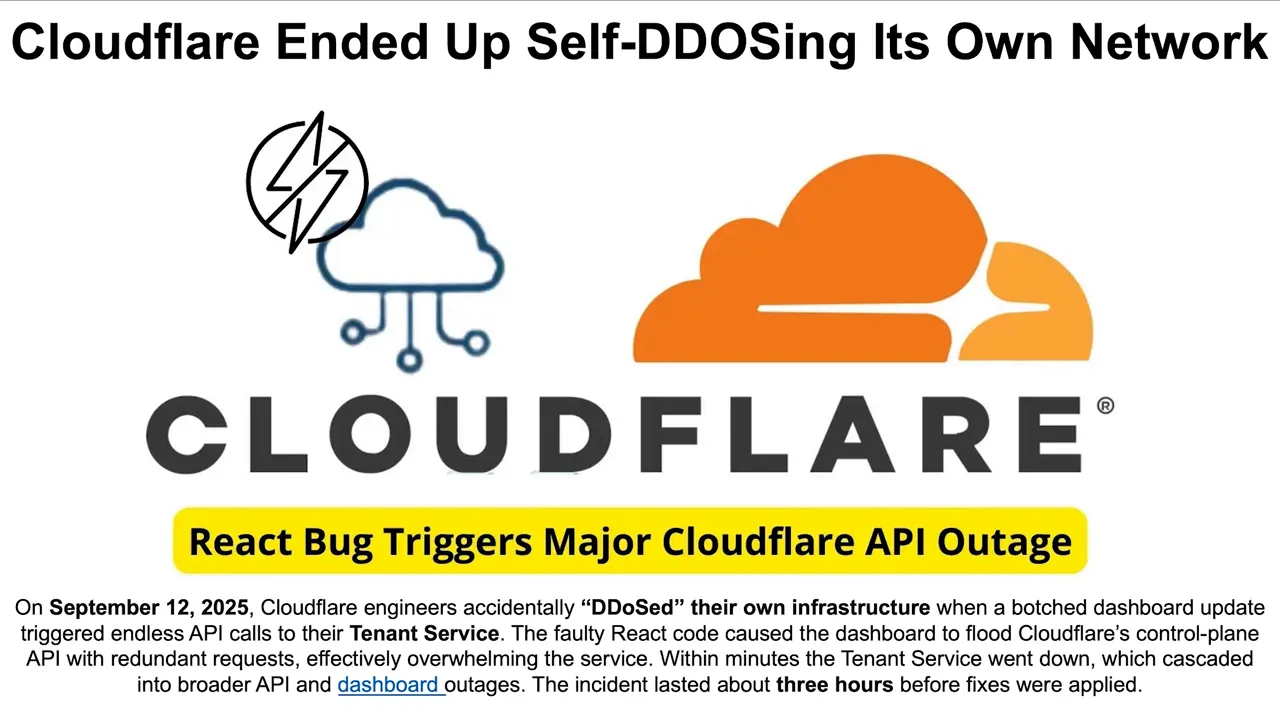
Resiliency matters, and yet we still underestimate how fragile the digital world is. A single API failure can cascade across industries: flights delayed, nurses locked out of medication charts, government services unavailable. Recent incidents include a Crowdstrike outage that caused widespread disruption, a Google outage in June 2025 triggered by a null pointer exception, Cloudflare incidents where a frontend retry loop overwhelmed tenant services, and a Tesla API outage that left owners unable to open their cars.

These stories are not edge cases. They are a warning: APIs are the fabric of our digital ecosystem. When an API goes down, everything built on top of it can come crashing down. That reality makes API resiliency testing not optional but essential.
What API resiliency testing actually means
At its core, API resiliency testing is about ensuring services are predictable and durable under adverse conditions. It is not just checking happy paths. Resiliency testing spans a spectrum of approaches designed to expose weaknesses before they fail in production.
The spectrum of resiliency tests
Think of resiliency testing as layers, each answering different failure questions. A good program includes several complementary techniques:
- Negative functional testing: boundary value analysis, invalid data types, overflow and underflow checks to make sure the API rejects bad input safely.
- Contract and compatibility checks: validate that downstream services remain contract compliant and that breaking changes are detected and handled gracefully.
- Timeouts and latency scenarios: test how your service behaves when dependencies respond slowly or not at all.
- Chaos and fault injection: intentionally inject failures, latency, dropped connections, and misrouted traffic to verify fallback logic and failover behavior.
- Load and stress testing: push the system to and beyond expected limits to reveal bottlenecks and degradation patterns.
- SOC testing: leave the system running under realistic load for long durations to detect resource leaks and gradual performance deterioration.
- Security testing: ensure resiliency against malicious inputs, DDoS scenarios, and abuse that can make services unavailable.
Why SOC testing often catches what others miss
Short bursts of load and unit tests are useful, but many faults only surface over time. SOC testing involves maintaining realistic traffic patterns and background processes for extended periods. This reveals memory leaks, slow-growing CPU usage, resource exhaustion, and database connection pool depletion.

You would be surprised how often long-running tests expose issues that never appear in short-run suites. Treat SOC testing as a core part of API resiliency testing, not an optional afterthought.
Real failure modes to prepare for
The recent Cloudflare incidents where frontend code triggered infinite retries, and the Google outage caused by a trivial null pointer exception, show how small bugs can cascade into major outages. A faulty client retry loop or an unchecked exception in a control plane can amplify load, overwhelm upstream services, and bring dashboards and APIs down for hours.
The Tesla API outage demonstrates a different consequence: user safety and trust. Failure can be inconvenient or dangerous. Designing for graceful degradation and safe defaults is part of being resilient.

Practical checklist for API resiliency testing
- Define failure scenarios: map dependencies and list what can go wrong (timeouts, bad data, schema changes, slow responses, full disk).
- Run negative functional tests: feed invalid inputs, unexpected types, and boundary values to every endpoint.
- Simulate dependency failures: emulate downstream timeouts, partial responses, and protocol errors.
- Inject faults in production-like environments: use chaos engineering tools to exercise circuit breakers, retries, and fallbacks.
- Include long-duration SOC tests: look for resource leaks and gradual degradation.
- Stress test at scale: validate throttling, rate limiting, and backpressure strategies.
- Run security and abuse scenarios: evaluate how your API behaves under attack patterns.
Monitoring and observability are non negotiable
Testing alone is not enough. Without meaningful monitoring and alerts you are flying blind. Observability provides the early warning systems you need: logs, metrics, traces, and anomaly detection that tell you something is going wrong before customers call support.

Effective alerts focus on actionable signals, not noisy thresholds. Combine health checks with business metrics so you know whether degraded performance actually impacts users. Good observability shortens detection and recovery times, making your resiliency investments pay off.
“When an API goes down, everything that sits on top of it comes crashing down.”
Putting it together: design for graceful failure
Resiliency is both engineering and mindset. Build APIs with clear contracts, defensive coding, timeouts, retries with backoff, circuit breakers, bulkheads, and sensible defaults. Test each of these behaviors regularly using automated suites and long-running experiments. Use observability to verify assumptions and learn from incidents.
Integrate API resiliency testing into your CI/CD pipeline so resilience checks are first class, not an afterthought. Small investments in testing, monitoring, and design pay exponential dividends when they prevent the next domino from falling.
FAQ
What is API resiliency testing?
API resiliency testing is a collection of tests and practices designed to ensure APIs remain available and predictable under adverse conditions, including invalid inputs, downstream failures, load spikes, and extended runtime issues.
Which types of tests should I prioritize?
Start with negative functional tests, contract checks, timeout and latency simulations, chaos experiments, load and stress tests, and long-duration SOC testing. Combine these with security tests and robust observability.
What is SOC testing and why is it important?
SOC testing means running systems under realistic conditions for an extended period to detect slow-developing problems such as memory leaks, resource exhaustion, and gradual CPU increase. It often uncovers issues missed by short tests.
How does observability fit into resiliency?
Observability provides the signals—logs, metrics, traces, and anomaly detection—needed to detect issues early, understand root causes, and automate responses. Without it, detection and recovery times increase dramatically.
How do I get started integrating resiliency tests into CI/CD?
Automate unit and integration tests that include negative cases and contract validations. Add chaos and fault injection in staging. Schedule SOC and load tests as part of a regular pipeline or nightly runs. Ensure test results feed back into issue tracking and release gating.